In the ever-evolving cyber threat landscape, cryptography remains a cornerstone of secure communication, data integrity, and identity assurance. However, cryptography isn’t a set-it-and-forget-it technology—mismanagement can lead to serious security exposures.
When cryptographic assets are poorly governed, attackers exploit these weaknesses using well-documented Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) cataloged in the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
In this blog, we explore how robust cryptographic hygiene, and key management can help defend against various stages of adversary activity mapped in MITRE ATT&CK. Specifically, we will highlight how deploying InfoSec Global Federal’s AgileSec™ Analytics platform will enable your enterprise to manage the posture of your cryptography and mitigate attacks against this critical surface area of attack.
Why Cryptographic Posture Management Matters
Cryptographic assets—like X.509 certificates, private keys, symmetric keys, and tokens—are foundational to authentication, encryption, code integrity, and digital signing. When these assets are exposed, expired, misconfigured, or weak, attackers can:
- Bypass authentication mechanisms
- Decrypt sensitive data
- Masquerade as trusted services
- Inject malicious code into secure channels
Proper cryptographic posture management (CPM) involves continuous inventory, lifecycle management, rotation, and policy enforcement across all cryptographic assets. Done right, this reduces the attack surface across many ATT&CK techniques.
MITRE ATT&CK TTPs Impacted by Cryptographic Mismanagement
Below is a breakdown of key TTPs in the MITRE ATT&CK framework that can be mitigated through strong cryptographic practices:
| Tactic | Technique | Technique ID | How Cryptography Helps |
| Initial Access | Exploit Public-Facing Application | T1190 | TLS enforcement, certificate pinning, and signed updates help prevent unauthorized access. |
| Execution | Signed Binary Proxy Execution | T1218 | Code signing integrity ensures binaries are verified before execution. |
| Persistence | Valid Accounts | T1078 | PKI-backed MFA and certificate-based authentication reduce password compromise risk. |
| Privilege Escalation | Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism | T1548 | Application whitelisting with verified signatures blocks unsigned privilege escalation. |
| Defense Evasion | Obfuscated Files or Information | T1027 | Encrypted data at rest with key rotation ensures adversaries can’t decrypt stolen assets. |
| Credential Access | Credential Dumping | T1003 | Encrypting credentials with hardware-based secure storage (e.g., TPM, HSM) reduces risk. |
| Discovery | Remote System Discovery | T1018 | Network encryption (TLS/mTLS) hides discovery attempts from attackers. |
| Lateral Movement | Pass the Hash / Pass the Ticket | T1550 | Session tokens and tickets should be encrypted, short-lived, and bound to endpoints. |
| Command & Control | Encrypted Channel | T1573 | Inspection of certificate chains and use of TLS interception on proxies detects anomalies. |
| Exfiltration | Exfiltration Over Encrypted Channel | T1041 | Strong egress controls and TLS inspection prevent abuse of encrypted tunnels. |
| Impact | Data Encrypted for Impact (Ransomware) | T1486 | File-level encryption policies and endpoint key controls limit blast radius. |
Cryptographic Posture Management Practices for TTP Mitigation
To defend against these TTPs, security teams must adopt cryptographic posture management, including:
- Automated Cryptographic Discovery and Inventory
- Automatically discover all cryptographic assets (certs, keys, tokens) across cloud, apps, devices, and workloads.
- Detect shadow or orphaned keys and certificates.
- Lifecycle Management
- Enforce expiration dates, rotate keys regularly, and decommission unused credentials.
- Replace weak cryptographic algorithms (e.g., SHA-1, RSA-1024) with strong alternatives.
- Access Controls
- Apply least privilege and RBAC to keys and crypto services.
- Use HSMs, TPMs, or secure enclaves to protect private keys.
- Monitoring & Alerting
- Detect anomalous usage or expired/compromised credentials.
- Log and audit all cryptographic operations.
- Policy Enforcement
- Define and enforce crypto policies across teams (e.g., FIPS-compliant algorithms only).
- Prevent deployment of self-signed or unauthorized certificates.
AgileSec™ Analytics
While MITRE ATT&CK helps security teams understand adversary behavior, good cryptographic posture management addresses the root causes of many exploitable vectors. It’s not just about confidentiality—it’s about trust, control, and reducing attacker options at every phase of the kill chain.
CPM must become a core element of an agency’s (or any enterprise’s) risk management.
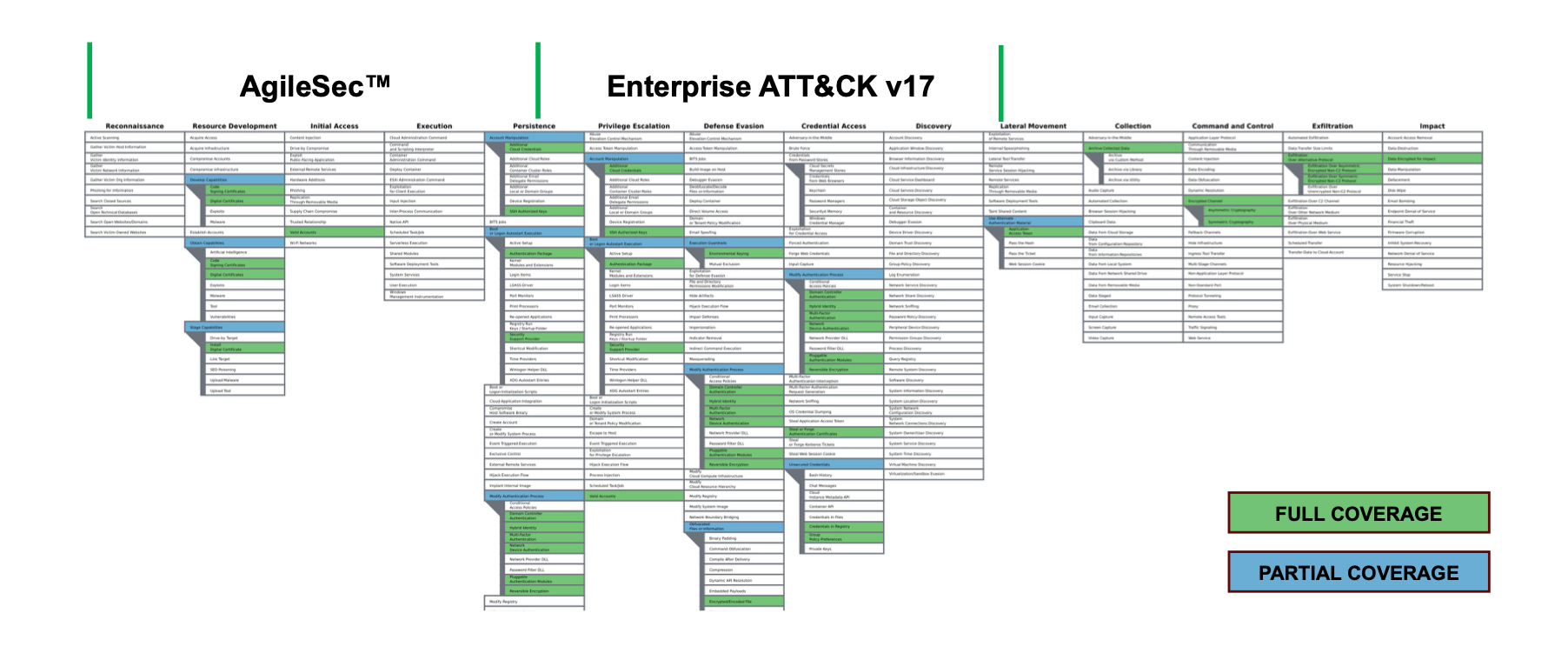
The first step in proper CPM is Automated Cryptographic Discovery and Inventory. Our AgileSec platform and, specifically our Analytics solution, offers the most comprehensive inventory and analytics capability in the industry. We’ve recently performed an analysis of MITRE TTP’s and identified the following potential mitigations by deploying AgilleSec Analytics:
Taking a closer look, we’ve done further analysis to identify the likely top MITRE ATT&CK TTP’s from cryptographic vulnerabilities along with the appropriate AgileSec Analytics control and examples of where these types of attacks have been performed:
| TTP | Description | AgileSec Control | Real-World Observation |
| T1480.001
Defense Evasion Execution Guardrails Environmental Keying |
Environmental keying uses cryptography to constrain execution or actions based on adversary-supplied environment-specific conditions that are expected to be present on the target. Environmental keying is an implementation of Execution Guardrails that utilizes cryptographic techniques for deriving encryption/decryption keys from specific types of values in a computing environment. | Identify encrypted rogue files; identify rogue crypto packages | The Russia-based LummaC2 malware tool seeks to bypass standard EDR and AV solutions by leveraging encryption. |
| T1550.001
Defense Evasion Use Alt Authentication Material Application Access Token |
Adversaries may use stolen application access tokens to bypass the typical authentication process and access restricted accounts, information, or services on remote systems. | Detect lack of Azure AD token protection or OAuth proof of possession usage | The transition to containerization in support of cloud scalablity and efficiencies has created thrust container registries front and center for malicious targeting of S3 keys, CSP access keys, database authentication credentials and JSON web tokens. |
| T1550.001
Defense Evasion, Lat. Movement Use Alt Authentication Material Application Access Token |
Adversaries may use stolen application access tokens to bypass the typical authentication process and access restricted accounts, information, or services on remote systems. These tokens are typically stolen from users or services and used in lieu of login credentials. | Detect lack of Azure AD token protection or OAuth proof of possession usage | Microsoft notified a large backup provider of suspicious activity within its Azure tenant. What was initially perceived as authorized access turned out to be APT abuse of authorized application access tokens resulting in a successful LoL attack and cross-tenant access to data and accounts. |
| T1573.002
Command and Control Encrypted Channel Asymmetric Cryptography |
Adversaries may employ an encryption algorithm to conceal command and control traffic rather than relying on any inherent protections provided by a communication protocol. Adversaries may employ a known asymmetric encryption algorithm to conceal command and control traffic rather than relying on any inherent protections provided by a communication protocol. | Identify rogue cryptographic packages | Blacksuit (royal) ransomware leverages partial encryption tactics to evade detection for data exfiltration and command and control sessions. |
| T1486
Impact Data Encrypted for Impact |
Adversaries may encrypt data on target systems or on large numbers of systems in a network to interrupt availability to system and network resources. They can attempt to render stored data inaccessible by encrypting files or data on local and remote drives and withholding access to a decryption key. | Identify rogue cryptographic packages (ex ransomware) | Play Ransomware evades detection by recompiling itself for each attack, resulting in unique hashes for every deployment. Following exfiltration of targeted data the remaining files are encrypted with AES-RSA hybrid encryption using intermittent encryption, encrypting every other file portion of 0x100000 bytes. |
| T1480.001
Defense Evasion Execution Guardrails Environmental Keying |
Environmental keying uses cryptography to constrain execution or actions based on adversary-supplied environment-specific conditions that are expected to be present on the target. Environmental keying is an implementation of Execution Guardrails that utilizes cryptographic techniques for deriving encryption/decryption keys from specific types of values in a computing environment. | Identify encrypted rogue files; identify rogue crypto packages | The Russia-based LummaC2 malware tool seeks to bypass standard EDR and AV solutions by leveraging encryption. |
| T1550.001
Defense Evasion Use Alt Authentication Material Application Access Token |
Adversaries may use stolen application access tokens to bypass the typical authentication process and access restricted accounts, information, or services on remote systems. | Detect lack of Azure AD token protection or OAuth proof of possession usage | The transition to containerization in support of cloud scalablity and efficiencies has created thrust container registries front and center for malicious targeting of S3 keys, CSP access keys, database authentication credentials and JSON web tokens. |
| T1550.001
Defense Evasion, Lat. Movement Use Alt Authentication Material Application Access Token |
Adversaries may use stolen application access tokens to bypass the typical authentication process and access restricted accounts, information, or services on remote systems. These tokens are typically stolen from users or services and used in lieu of login credentials. | Detect lack of Azure AD token protection or OAuth proof of possession usage | Microsoft notified a large backup provider of suspicious activity within its Azure tenant. What was initially perceived as authorized access turned out to be APT abuse of authorized application access tokens resulting in a successful LoL attack and cross-tenant access to data and accounts. |
| T1573.002
Command and Control Encrypted Channel Asymmetric Cryptography |
Adversaries may employ an encryption algorithm to conceal command and control traffic rather than relying on any inherent protections provided by a communication protocol. Adversaries may employ a known asymmetric encryption algorithm to conceal command and control traffic rather than relying on any inherent protections provided by a communication protocol. | Identify rogue cryptographic packages | Blacksuit (royal) ransomware leverages partial encryption tactics to evade detection for data exfiltration and command and control sessions. |
| T1486
Impact Data Encrypted for Impact |
Adversaries may encrypt data on target systems or on large numbers of systems in a network to interrupt availability to system and network resources. They can attempt to render stored data inaccessible by encrypting files or data on local and remote drives and withholding access to a decryption key. | Identify rogue cryptographic packages (ex ransomware) | Play Ransomware evades detection by recompiling itself for each attack, resulting in unique hashes for every deployment. Following exfiltration of targeted data the remaining files are encrypted with AES-RSA hybrid encryption using intermittent encryption, encrypting every other file portion of 0x100000 bytes. |
Final Thoughts
Cryptography is not just an IT concern—it’s a strategic enabler of security resilience. When governed well, it acts as a control plane to contain attacker movement and protect critical systems from compromise. Organizations seeking to align with the MITRE ATT&CK framework must elevate their crypto hygiene as part of a broader threat-informed defense strategy.